

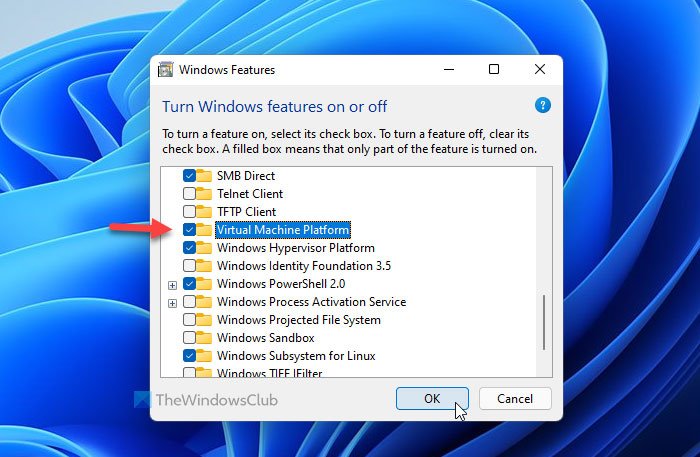
You will find it in WSA settings under System > Memory and performance. The option is called " Memory allocation".
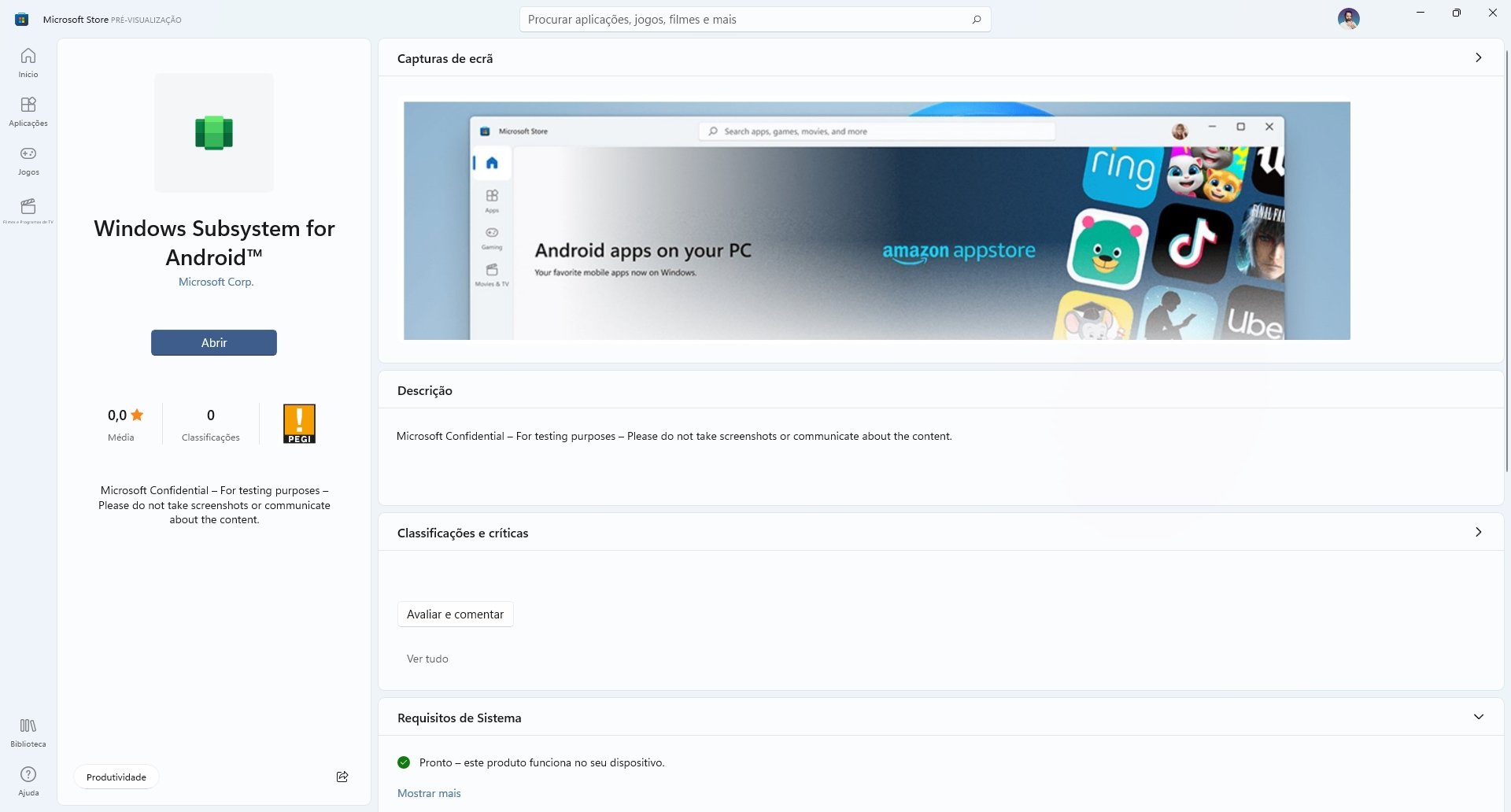
This updated app includes improvements to reliability, adds package verification and AppLink support.Īfter installing this update, users can specify how much system memory is available to WSA. Windows Insiders can now access the latest version of Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA), version 2304.40000.3.0. We have reached out to Microsoft for comment, and this story will be updated if we hear anything more from the company.RЕCOMMENDED: Click here to fix Windоws issues and optimize system performance

Microsoft officials confirmed Android apps will be enabled in future builds of Windows 11 and the first preview build will not include Android Subsystem for Windows.Īt the moment, it’s unclear exactly how the APK sideloading process will work on Windows and whether Microsoft is working on a special installer for mobile apps. Amazon Appstore will be integrated into Microsoft Store for Android apps section and all users will have access to the Amazon marketplace, but there’s a catch – not every Android app in the Appstore will run on Windows 11. To better support Android apps on Windows, Microsoft is working with Amazon to bring its Appstore to Windows 11. This is one of the key upgrades for WSL2 over WSL1. Since WSA is based on advancements from Project Astoria and WSL2, performance is expected to be better than the traditional emulators available in the market. Microsoft is also integrating a virtual machine that would enable compatibility for the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). WSA is similar to the existing Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) and it will provide support for “proxy” between the native app container and Android app. Using the WSL technology, Microsoft has now created Windows Subsystem for Android to run mobile apps on the desktop. With Windows 11, Microsoft is introducing two new features – GUI support for WSL and WSA (Windows Subsystem for Android).
On Windows 11, WSL2 runs on its own kernel, device drivers, kernel modules, and users can even place their Linux files within the root file system. As you’re probably, Windows comes with its own subsystem for Linux (WSL), which was introduced back in 2016.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
